Science Lesson: Engineering Wind Turbines
In this lesson, students use what they know about magnets, forces, energy transfer, and generators to engineer a vertical-axis wind turbine that generates a specific amount of electrical energy in both low and high wind speeds.
Science Big Ideas
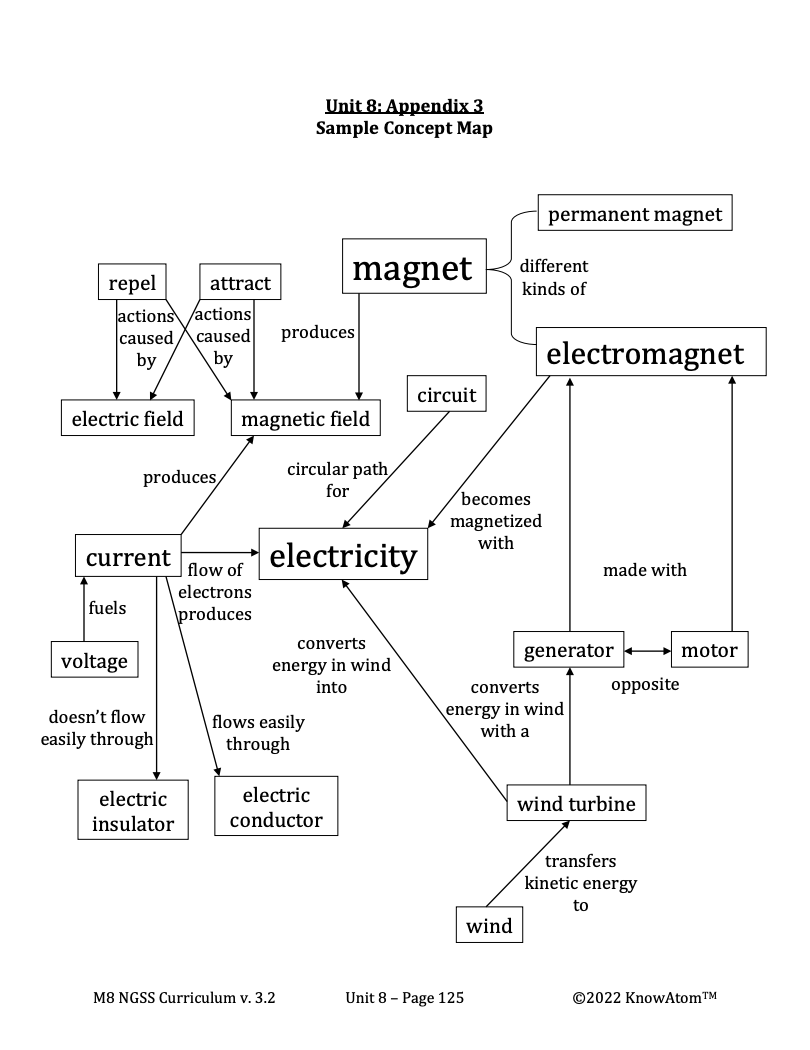
- Electric motors and generators are important in technologies that produce the electricity our society depends on. A generator is a machine that converts an input of kinetic energy into an output of electrical energy.
- Wind turbines are devices that convert kinetic energy from the wind into electrical power. Wind has energy because it is moving air molecules, and wind turbines are designed to capture this energy.
- There are two basic designs of wind turbines: vertical-axis turbines and horizontal-axis turbines.
- Engineers are always looking for ways to design technologies that transform energy as efficiently as possible because they want to generate more work while using less energy.
- Engineers need to think about a variety of factors, including location and energy efficiency, when designing wind turbines.

Discover Complete Hands-on Screens-off Core Science Curriculum for K-8 Classrooms
Prepared hands-on materials, full year grade-specific curriculum, and personalized live professional development designed to support mastery of current state science standards.
Science Essential Questions
- How would you describe the inputs and outputs of energy in a generator?
- How is a generator similar to a motor?
- Why does wind have kinetic energy?
- How is the kinetic energy in wind useful for people?
- How is the kinetic energy of the wind captured by a wind turbine?
- How can the turning blades cause kinetic energy to convert into electrical energy?
- Why is energy efficiency important in wind turbines?
- Why aren’t horizontal-axis turbines always the best choice for a wind turbine design?
- Why are vertical-axis turbines more common in urban areas?
Common Science Misconceptions
Misconception: Electric charges and magnetic poles are the same thing so magnets can be attracted to or repulsed by electric charge.
Fact: Electric charges are different from magnetic poles, and do not affect magnets or magnetic materials.
Science Vocabulary
Generator : a machine that converts an input of kinetic energy into an output of electrical energy
Motor : a machine that transfers an input of electrical energy into an output of kinetic energy
Wind : moving air molecules
Wind turbine : a device that converts kinetic energy from the wind into electrical power
Lexile(R) Certified Non-Fiction Science Reading (Excerpt)
Mimicking Animals
Many engineers have studied the wings of hummingbirds because of their amazing flight abilities. They are the only birds that can fly both forward and backwards. They can also hover in mid-air, fly sideways, and even upside-down.
For example, engineers in North Africa are developing wind turbines that mimic the hummingbird’s wings as it hovers. A wind turbine is a device that converts kinetic energy from the wind into electrical power.
Other engineers have looked to other animals for inspiration about the shape of their wind turbines. Humpback whales and schools of fish have also inspired different designs, from the shape of the blades to their placement on the tower and the relationship of each turbine relative to the other turbines.
The Search for Efficiency
The main reason that engineers are searching for new ways to design wind turbines is to improve their efficiency. In any energy system where energy is being converted from one form to another, not all of the energy is converted to a form that can do work. Some is usually transformed into non-usable forms of energy.
A simple example of this is moving a box across the floor. You, the box, and the floor form an energy system. As you push the box, you are providing an input of force that transfers kinetic energy to the box. This kinetic energy is what causes the box to move.
However, as the box moves across the floor, the force of friction transfers energy out of the system by causing some of the energy of the moving object to change into heat. The more friction there is, the less efficient your energy system is because less kinetic energy is available to do the work of moving the box.
Engineers are always looking for ways to design technologies that transform energy as efficiently as possible. They want to generate more work while using less energy. This is true for wind turbines, which capture the kinetic energy of the wind.



Hands-on Science Activity
For the engineering challenge in this lesson, students use the engineering design process to design and build a vertical-axis wind turbine that generates a specific amount of electrical energy in low and high wind speeds. Additionally, students evaluate how engineers use scientific concepts and knowledge to design technologies that solve problems.
Science Assessments
KnowAtom incorporates formative and summative assessments designed to make students thinking visible for deeper student-centered learning.
- Vocabulary Check
- Lab Checkpoints
- Concept Check Assessment
- Concept Map Assessment
- And More...

See How KnowAtom Aligns to NGSS Science Standards
Discover hands-on screens-off core science curriculum for student centered K-8 classrooms. KnowAtom supports classrooms with all hands-on materials, curriculum, and professional development to support mastery of the standards.

