Science Lesson: Exploring Photosynthesis and Oil Spills
Once students model how energy flows through ecosystems, they focus on the source of this energy: the sun. Plants harness that energy through the phenomena of photosynthesis, and therefore play a critical role in all food webs. Students create an experiment to investigate how a disturbance such as an oil spill affects the ability of plants to photosynthesize.
Science Big Ideas
- The ability of plants to access sunlight is important for the entire food web because plants turn sunlight, along with carbon dioxide and water, into glucose and oxygen.
- Photosynthesis is connected to the oxygen cycle, which is the back-and-forth exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between plants, animals, and the environment.
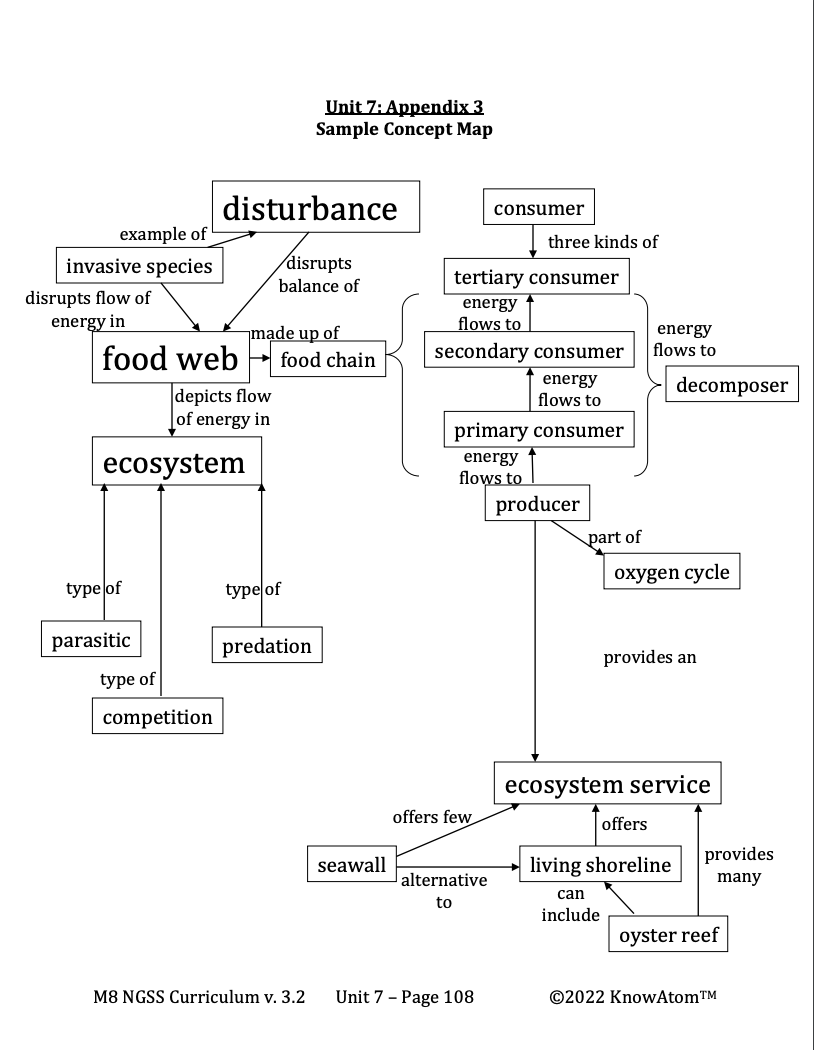
- A change to the ecosystem that removes an energy source will have a ripple effect throughout the ecosystem, just as the introduction of an invasive species impacts all levels of the food web.
- Oil spills can cause serious harm to ecosystems.

Discover Complete Hands-on Screens-off Core Science Curriculum for K-8 Classrooms
Prepared hands-on materials, full year grade-specific curriculum, and personalized live professional development designed to support mastery of current state science standards.
Science Essential Questions
- Why are plants important in food webs?
- Why are there always more producers than consumers in a food web?
- How do plants use carbon dioxide? How do animals use carbon dioxide?
- How do plants use oxygen? How do animals use oxygen?
- How else does carbon cycle between living things?
- How can oil get into the environment?
- How does an oil spill affect the environment?
Common Science Misconceptions
Misconception: Ecosystems are static.
Fact: Ecosystems are dynamic and constantly changing.
Science Vocabulary
Competition : an interaction between organisms that occurs whenever two or more organisms require the same limited resource
Disturbance : an event that changes conditions in an ecosystem
Ecosystem : a community of different species that depend on interacting with each other and their physical environment for survival
Invasive species : non-native species that disrupt the flow of energy through an ecosystem
Oxygen cycle : a back-and-forth exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between plants, animals, and the environment
Lexile(R) Certified Non-Fiction Science Reading (Excerpt)
Gulf of Mexico Oil Spill
One of the largest marine oil spills happened in 2010 in the Gulf of Mexico. An oil rig called the Deepwater Horizon exploded and sank. This caused oil to gush into the ocean for 87 days. Eleven people died. Estimates put the amount of oil spilled at 4.9 million barrels, equal to 210 million gallons.
The spill was devastating to the gulf’s diverse ecosystems. These ecosystems include coastal wetlands, underwater canyons, ocean water, and fresh water from rivers in the United States and Mexico. Killer whales, shrimp, oysters, migrating waterfowl, and deepwater coral all live in the Gulf of Mexico. More than 6,000 birds, 600 sea turtles, and 100 mammals were killed as a result of the oil spill.
Long-Term Effects of Deepwater Horizon
Scientists are still trying to figure out the long-term effects of the oil spill. The complex interactions between all of the living things in the Gulf of Mexico and their environment make it difficult for scientists to fully understand the long- term effects of the spill on the ecosystem.
Ecosystem Disturbances
Any event that changes conditions in an ecosystem is called a disturbance. There are many kinds of disturbances that affect ecosystems. Fires, floods, volcanic eruptions, and extreme weather such as drought and tornadoes are all disturbances. These events can lead to shifts of resources within an ecosystem. They can also affect the populations of organisms that make up the ecosystem.
How energy flows through an ecosystem determines which organisms will live and which will die. Because of this, a change to the ecosystem that removes an energy source will have a ripple effect throughout the ecosystem. This is similar to how the introduction of an invasive species impacts all levels of the food web.
The Importance of Photosynthesis
When a plant captures light energy from the sun and carries out photosynthesis, it uses 90 percent of the energy to perform all of its life functions. This leaves 10 percent of the energy to get passed along to consumers. Because primary consumers only get 10 percent of the energy, they must eat more plants to get enough energy to perform all of their life functions. When a secondary consumer eats a primary consumer, only 10 percent of this energy gets passed along. The decreasing amount of available energy as you move up a food web explains why there are fewer organisms at the top of a food chain than at the bottom.
Energy gets passed along in the form of chemical bonds holding together the molecules of glucose. Each cell in every living thing takes the glucose and performs cellular respiration in its mitochondria. Remember that cellular respiration is the process in which cells extract energy from food. Oxygen is used to break down the glucose so its energy can be stored in molecules of ATP. ATP is the molecule that powers life. In addition to ATP, cellular respiration also produces heat and carbon dioxide as by-products.
This transfer of energy from one organism to another explains why energy moves in one direction through an ecosystem. It also explains why life requires a constant supply of energy from the sun.



Hands-on Science Activity
In this lesson, students develop an experiment to examine how an oil spill alters the cycling of matter and the flow of energy through an ecosystem phenomena by disrupting the ability of aquatic plants to photosynthesize. This gives students the opportunity to experiment and evaluate the importance of producers to all food web phenomena because of their ability to capture the sun’s energy.
Science Assessments
KnowAtom incorporates formative and summative assessments designed to make students thinking visible for deeper student-centered learning.
- Vocabulary Check
- Lab Checkpoints
- Concept Check Assessment
- Concept Map Assessment
- And More...

See How KnowAtom Aligns to NGSS Science Standards
Discover hands-on screens-off core science curriculum for student centered K-8 classrooms. KnowAtom supports classrooms with all hands-on materials, curriculum, and professional development to support mastery of the standards.

