Science Lesson: Designing and Building as Engineers
In this lesson students use what they know about how sunlight warms Earth’s surface to design a prototype solution that helps people stay cool on a hot, sunny beach. Students first explore the work of an engineer through a circle-time book, then they discuss the importance of engineering, before working in pairs to solve a problem. Students plan, design, build, test, and analyze the prototype they create to fully experience the engineering cycle.
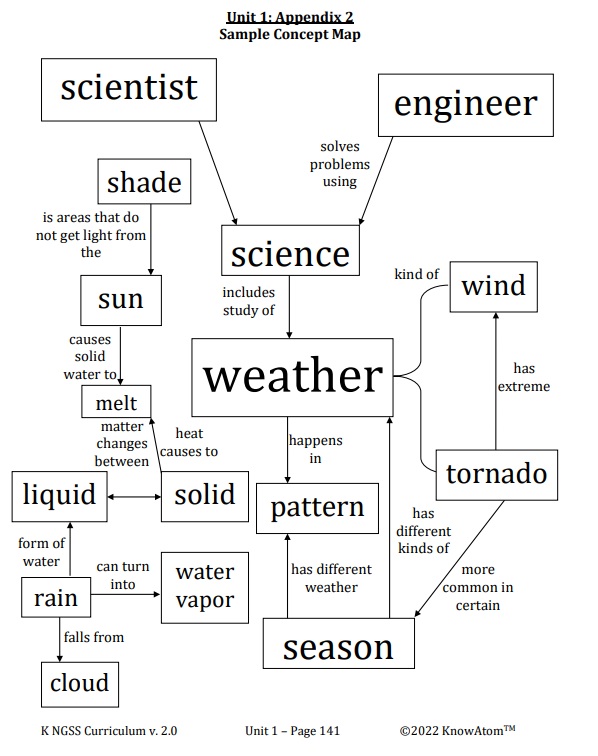
Science Big Ideas
- Engineers are people who solve problems by designing solutions to those problems.
- Engineers can use scientific concepts to reduce the warming effect of sunlight on Earth’s surface.
- Engineers first understand the problem, then plan and design a prototype solution, and finally test their prototype before making changes to improve it.

Discover Complete Hands-on Screens-off Core Science Curriculum for K-8 Classrooms
Prepared hands-on materials, full year grade-specific curriculum, and personalized live professional development designed to support mastery of current state science standards.
Science Essential Questions
- What makes a scientist different from an engineer?
- What are some examples of engineering around us?
- What is an example of a problem that an engineer has solved?
- Why do engineers need scientific knowledge?
- What scientific knowledge have you learned about how different materials are heated by the sun?
Common Science Misconceptions
Misconception: Engineers and scientists are the same.
Fact: Engineers and scientists use many of the same practices and skills, but they have different goals. Scientists search for answers to questions, while engineers solve problems.
Science Vocabulary
Engineer : a person who uses scientific knowledge to solve problems
Lexile(R) Certified Non-Fiction Science Reading (Excerpt)


Hands-on Science Activity
In this hands-on activity, students will work in pairs to design a prototype to create shade from the sun on a beach. Students are given an engineering problem and they must plan, design, build and test a prototype to solve the problem. The goal of this activity is for students to experience the engineering design-solution process. After students test their prototype to see how well it solves the problem, students discuss possible improvements and make changes accordingly. Students will continue to practice this engineering process in future grades.
Science Assessments
KnowAtom incorporates formative and summative assessments designed to make students thinking visible for deeper student-centered learning.
- Vocabulary Check
- Lab Checkpoints
- Concept Check Assessment
- Concept Map Assessment
- And More...

See How KnowAtom Aligns to NGSS Science Standards
Discover hands-on screens-off core science curriculum for student centered K-8 classrooms. KnowAtom supports classrooms with all hands-on materials, curriculum, and professional development to support mastery of the standards.

