In this unit, students explore the science phenomena of different processes that change Earth’s surface over time. Once students have investigated how wind and water change the shape of the land, they use their scientific knowledge to engineer a solution that prevents rainwater from washing away a sandy hillside. This page showcases key components of this lesson.

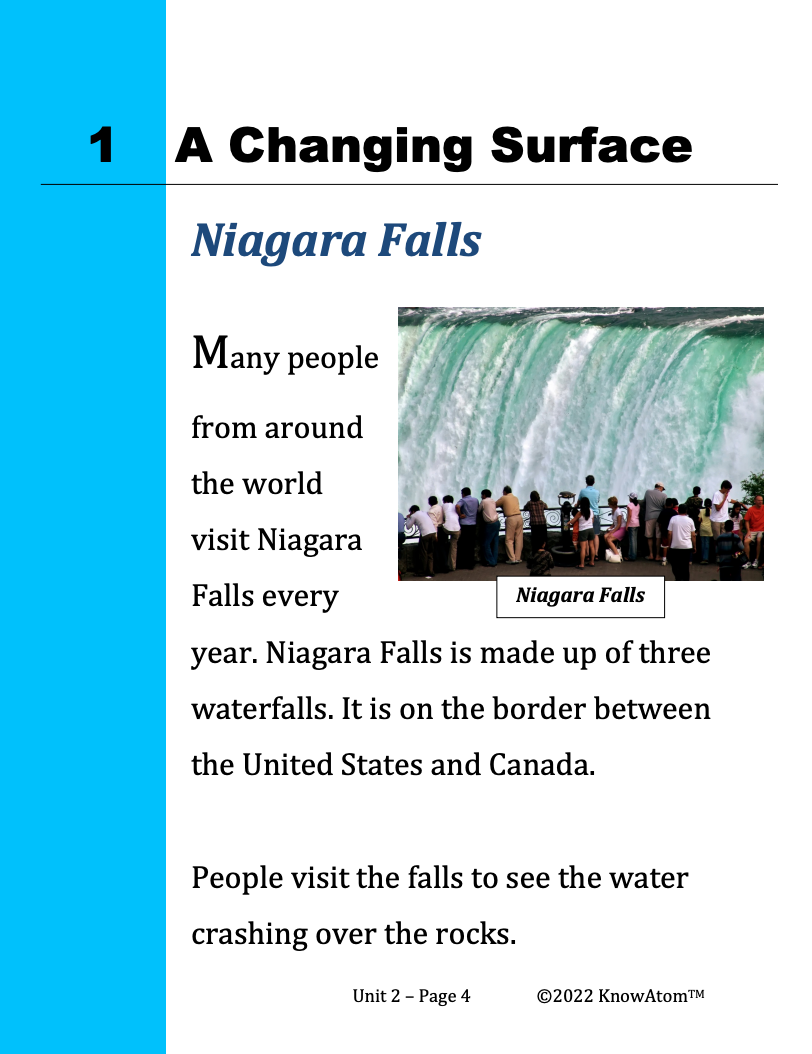
In the last unit, students explored how weathering and erosion change Earth materials, and then designed an engineering solution that reduces erosion. In this unit, students are introduced to the science phenomena of landforms on Earth’s surface, exploring how scientists use maps to represent the shapes and kinds of land and water on Earth’s surface.

In kindergarten, students work towards developing routines and practices that scientists use to investigate phenomena and solve problems. This page is an extract from lesson 5 where students build on their weather observation skills as they observe and record local weather data to analyze weather patterns in their geographic area. Students continue to collect weather data over several months as they move onto the next lessons to build on their weather patterns analysis.

In this first unit, students learn to differentiate between the practices of a scientist and those of an engineer. Students ask questions, make observations, and collect data as they explore weather patterns on Earth and investigate how different Earth materials are heated by the sun. During this final lesson of the unit, students act as engineers by designing a prototype that can reduce the warming effects of the sun.

In this unit, students explore science phenomena related to patterns that result from Earth’s rotation and the moon’s orbit around the sun. This page provides a brief overview of lesson two of this unit, in which students conduct two investigations and use the patterns they discover to make predictions about the future positions of the sun, moon, and stars in the sky. In the first investigation, students observe the sun’s position in the sky at different times of day, drawing a diagram (model) of the sun’s position above the horizon. In the second investigation, students use a sundial model to explore the relationship between the sun’s position and the length of shadows.

In this unit, students investigate the science phenomena of seasonal patterns and water cycles. Once students have analyzed how seasonal patterns of sunrise and sunset can be observed and predicted, they focus on seasonal temperature and rainfall patterns. They investigate temperature patterns of a specific location throughout the year.
Standards citation: NGSS Lead States. 2013. Next Generation Science Standards: For States, By States. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press. Neither WestEd nor the lead states and partners that developed the Next Generation Science Standards were involved in the production of this product, and do not endorse it.