Science Lesson: Exploring Photosynthesis
In this lesson, students explore the phenomena of how plants cycle matter and energy through photosynthesis. They focus on plants in a forest as they create an experiment to test how different light conditions affect the rate of photosynthesis phenomena in aquatic plants.
Science Big Ideas
- Like all living things, plants need energy to grow and develop. However, unlike most other living things, including fungi and animals, plants make their own food using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water.
- Plants cycle both matter and energy in photosynthesis.
- Plants need sunlight to carry out photosynthesis because it is a chemical reaction. The sunlight is the input of energy that turns carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
- Different parts of the plant work together to collect what the plant needs to carry out photosynthesis.
- There are layers in any forest, and different amounts of energy reach each layer.
- A plant’s ability to carry out photosynthesis depends on how much sunlight it can access, which is partly dependent on which layer of the forest it is in.

Discover Complete Hands-on Screens-off Core Science Curriculum for K-8 Classrooms
Prepared hands-on materials, full year grade-specific curriculum, and personalized live professional development designed to support mastery of current state science standards.
Science Essential Questions
- How do plants get the energy they need to survive?
- What kinds of matter do plants need to take in to carry out photosynthesis?
- Where do plants get their source of energy to carry out photosynthesis?
- Why are a plant’s leaves important for photosynthesis?
- How does a plant get the water it needs to carry out photosynthesis?
- Why do plants take in minerals from the soil if they make their own food?
- Why do trees that grow in the canopy access most of the forest’s energy?
- Why is there less sunlight available in the understory?
- Why does the forest floor have even less sunlight than the understory?
Common Science Misconceptions
Misconception: Food must come from outside of an organism.
Fact: Plants make their own food through photosynthesis, unlike animals, which must eat other organisms for food.
Misconception: Healthy ecosystems do not change.
Fact: Healthy ecosystems are dynamic and constantly changing.
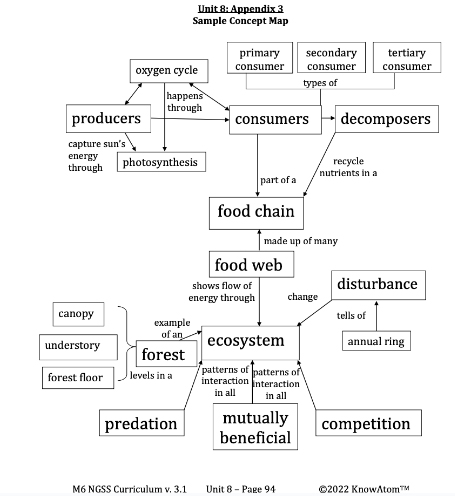
Science Vocabulary
Canopy : the upper layer of a forest where the treetops of most of the trees meet to form a layer of habitats for insects, birds, and tree-climbing mammals
Forest : an area of land covered by trees
Forest Floor : the part of the forest that is blanketed with decaying leaves, twigs, fallen moss, and other organic particles
Oxygen Cycle : the back-and-forth exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between plants, animals, and the environment
Photosynthesis : the process of turning sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into glucose and oxygen
Understory : the middle layer of the forest that contains a mixture of small and immature trees that provide shelter for animals
Lexile(R) Certified Non-Fiction Science Reading (Excerpt)
Studying How Trees Communicate
Scientist Suzanne Simard has been studying forests in Canada for 30 years. A forest is an area of land covered with trees. In 1997, Suzanne had a question: Do trees in a forest communicate with one another and share resources?
Her hypothesis was that trees in a forest are connected together in some kind of network. Suzanne designed an experiment to test her hypothesis. She focused on an area of the forest that had two kinds of trees: birch trees and fir trees.
Testing Trees and Carbon
She put plastic bags over individual trees. She then injected carbon-14 into one bag covering a birch tree to see if it would transfer some of the carbon to other trees nearby.
Carbon-14 is an isotope of carbon. This means it is one form of carbon. All isotopes of an element have the same number of protons, but they have a different number of neutrons. Carbon-12 is the most common form of carbon, making up 99 percent of all carbon in Earth’s atmosphere. Carbon-13 makes up 1 percent, and carbon-14 is found in trace amounts. Suzanne knew that carbon-14 molecules would bond with oxygen molecules in the environment to form carbon dioxide (CO2). She also knew that plants need carbon dioxide to survive.
Making Food
Plants need carbon dioxide because it is an important part of photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process of turning sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into glucose and oxygen. All plants carry out photosynthesis. This is how they make food. The glucose is a kind of sugar that holds chemical potential energy. Plants need this energy for growth and development.
Plants are constantly taking in carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen. This is similar to how people are always breathing, but people breathe in oxygen and release carbon dioxide. The back- and-forth exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between plants, animals, and the environment is called the oxygen cycle.



Hands-on Science Activity
For the hands-on activity of this lesson, students explore investigative phenomena on different light conditions and how they affect the rate of photosynthesis in aquatic plants. Students do this by measuring how much carbon dioxide aquatic plants remove from water. They then use the data to determine the relationship between the intensity of light and the ability of plants to carry out the phenomena of photosynthesis.
Science Assessments
KnowAtom incorporates formative and summative assessments designed to make students thinking visible for deeper student-centered learning.
- Vocabulary Check
- Lab Checkpoints
- Concept Check Assessment
- Concept Map Assessment
- And More...

See How KnowAtom Aligns to NGSS Science Standards
Discover hands-on screens-off core science curriculum for student centered K-8 classrooms. KnowAtom supports classrooms with all hands-on materials, curriculum, and professional development to support mastery of the standards.

