Science Lesson: Understanding Living Things in Their Habitat
In this lesson, students learn about animal habitats by creating a model of a forest habitat and analyzing the interaction between living and nonliving things in the model habitat. The goal of this model is for students to explore the relationships between the needs of plants and animals that live in a forest habitat.
Science Big Ideas
- Living things interact with other living things, as well as nonliving things in their habitat to survive.
- Plants and animals live in habitats that meet their specific needs.

Discover Complete Hands-on Screens-off Core Science Curriculum for K-8 Classrooms
Prepared hands-on materials, full year grade-specific curriculum, and personalized live professional development designed to support mastery of current state science standards.
Science Essential Questions
- What are the different parts that make up a forest habitat?
- What is a forest?
- How do forests help the animals that live there survive?
- How is an ocean habitat different from a forest habitat? How are they similar?
- Why are fish found in both an ocean and a forest habitat?
Common Science Misconceptions
Misconception: Plants are not alive because we cannot see them move.
Fact: Plants are alive because they meet all of the requirements for life. For example, there is movement within plants; we just cannot see it.
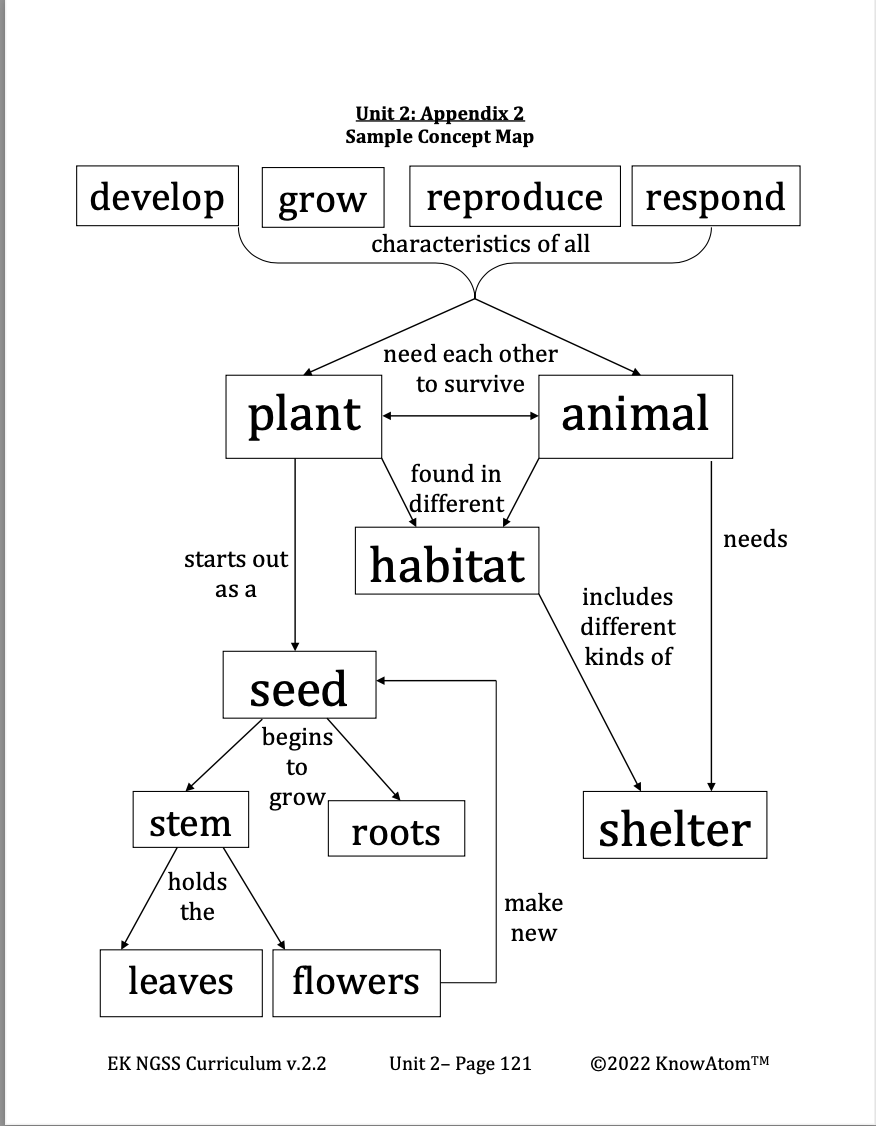
Science Vocabulary
Animal : a living thing that needs to eat other living things for energy and breathes in oxygen
Habitat : a place where life grows; provides plants and animals with clean water, air, food, and shelter
Shelter : a structure that protects animals from other animals and weather
Lexile(R) Certified Non-Fiction Science Reading (Excerpt)


Hands-on Science Activity
In this hands-on activity, students explore a forest habitat and discuss their observations of living and nonliving things they notice. For example, they may observe that the fish need a river or lake in their forest habitat to survive. Students connect the needs of the forest animals with all that the forest has to offer (e.g. shelter provided by the trees, water to drink, fruit from the trees for food). Towards the end of the mini-lesson, students discuss some predictions about what would happen if one element from the forest disappears and how this may affect the plants and animals living in the forest habitat.
Science Assessments
KnowAtom incorporates formative and summative assessments designed to make students thinking visible for deeper student-centered learning.
- Vocabulary Check
- Lab Checkpoints
- Concept Check Assessment
- Concept Map Assessment
- And More...

See How KnowAtom Aligns to NGSS Science Standards
Discover hands-on screens-off core science curriculum for student centered K-8 classrooms. KnowAtom supports classrooms with all hands-on materials, curriculum, and professional development to support mastery of the standards.

