Science Title: Distinguishing Living and Nonliving Things
In this lesson, students compare and contrast the characteristics that distinguish living things from nonliving and once living-things using picture cards.
Science Big Ideas
- Living things need food, energy, water, and air to survive.
- Living things eventually die, and although a dead plant might not look like a living thing, it was once living.
- Some things have some, but not all, of the requirements, and so they cannot be considered alive

Discover Complete Hands-on Screens-off Core Science Curriculum for K-8 Classrooms
Prepared hands-on materials, full year grade-specific curriculum, and personalized live professional development designed to support mastery of current state science standards.
Science Essential Questions
- What makes living things different from nonliving things?
- Why is food important for all living things?
- How do plants move, given that they cannot move from one place to another in the same way that animals do?
- How do animals move? Why do animals need to eat food to move?
- How do living things grow?
- Why do we need to drink water?
- How do animals breathe?
- How do plants breathe, given that they don’t have lungs in the same way that people do?
- What does it mean that all living things reproduce?
- Why were logs once living? Why is a dead insect once living?
- Why is fire nonliving? Why is a rock nonliving?
Common Science Misconceptions
Misconception: Plants get their food from the soil through their roots.
Fact: The leaves of plants absorb the sun’s energy, which allows them to make their own food through photosynthesis. Water and minerals are taken in through the roots.
Misconception: Sunlight helps plants grow by keeping them warm.
Fact: The sun’s energy is an important ingredient in the process that allows plants to make their own food. This is why the sun is so important for plant growth.
Science Vocabulary
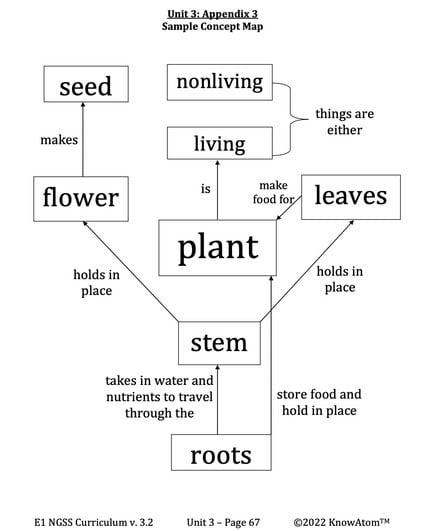
Flowers : the parts of a plant that make seeds
Leaves : the parts of a plant that collect sunlight and make food
Living : anything that breathes, needs food and water, grows, moves, and reproduces
Plant : a living thing that makes its own food from sunlight
Nonliving : anything that does not meet, and has never met, all of the requirements of life
Roots : the part of the plant that holds a plant in place and takes in nutrients and water from the soil
Seed : a young plant inside a protective coat; needs soil, water, and sunlight to grow
Stem : the part of a plant that holds the leaves and flowers in place; water and nutrients travel through the stem to the rest of the plant
Lexile@ Certified Non-Fiction Science Reading (Excerpt)
Food and Energy
Food is important. It helps living things grow. As they grow, living things get bigger. They get more complex.
The scientists who studied sunflowers carried out experiments. They learned that young sunflowers grow more when they follow the sun. The sunlight allows the plants to make food.
Food gives living things energy. Living things need energy to move. Some living things move in ways we can’t see. It happens in their bodies.
One side of a sunflower stem grows more during the day. The other side grows more at night. This causes the sunflower’s face to move so it follows the sun. Other living things use energy to move from place to place.
Water and Air
Living things need water. Our bodies use water for many things.
All living things breathe. This means they exchange gasses with the environment. Animals breathe in oxygen. They breathe out carbon dioxide. Plants take in carbon dioxide. They release oxygen.
All living things reproduce. This means they produce young. Humans have babies. Birds lay eggs. Many plants produce seeds that will grow into new plants. Young plants and animals are similar to their parents. They aren’t exactly the same though.



Hands-on Science Activity
For the hands-on activity of this lesson, students conduct an investigation to differentiate between living things, and nonliving or once-living things. They research and discuss the characteristics of living things before working collaboratively in small groups to sort things into living, nonliving, or once-living categories. Students discuss their reasoning behind each sorting decision and use their knowledge of living things to defend their claim.
Science Assessments
KnowAtom incorporates formative and summative assessments designed to make students thinking visible for deeper student-centered learning.
- Vocabulary Check
- Lab Checkpoints
- Concept Check Assessment
- Concept Map Assessment
- And More...

See How KnowAtom Aligns to NGSS Science Standards
Discover hands-on screens-off core science curriculum for student centered K-8 classrooms. KnowAtom supports classrooms with all hands-on materials, curriculum, and professional development to support mastery of the standards.

