Science Lesson: Modeling the Parts of Plants
In this lesson, students create models of adult sunflower plants to explore how plants have different parts that help them get what they need to survive. Students will use their understanding of plant parts and plant survival as they continue to learn about how plants grow and what they need to grow.
Science Big Ideas
- Plants are living things that make their own food from sunlight.
- Each part of a plant has an important role to play in keeping the plant alive.

Discover Complete Hands-on Screens-off Core Science Curriculum for K-8 Classrooms
Prepared hands-on materials, full year grade-specific curriculum, and personalized live professional development designed to support mastery of current state science standards.
Science Essential Questions
- What are some plants you have seen?
- What do all of these plants have in common?
- How would you describe a plant’s roots? Why do plants need roots?
- How would you describe a plant’s stem? Why is the stem important for plants?
- Why do plants need leaves?
- Why do you think plants grow their leaves above ground, while they grow roots underground?
- Where does a plant make its seeds?
Common Science Misconceptions
Misconception: Anything that moves is alive, while all nonliving things have died.
Fact: Not all moving things are living. Living things all have certain characteristics in common, including the ability to grow, exchange gasses with the environment, reproduce, excrete waste, and respond to stimuli, and all living things need energy to carry out these functions. Nonliving things do not meet all of the characteristics of life.
Misconception: Plants are not alive because we cannot see them move.
Fact: Plants are alive because they meet all of the requirements for life. For example, there is movement within plants; we just cannot see it.
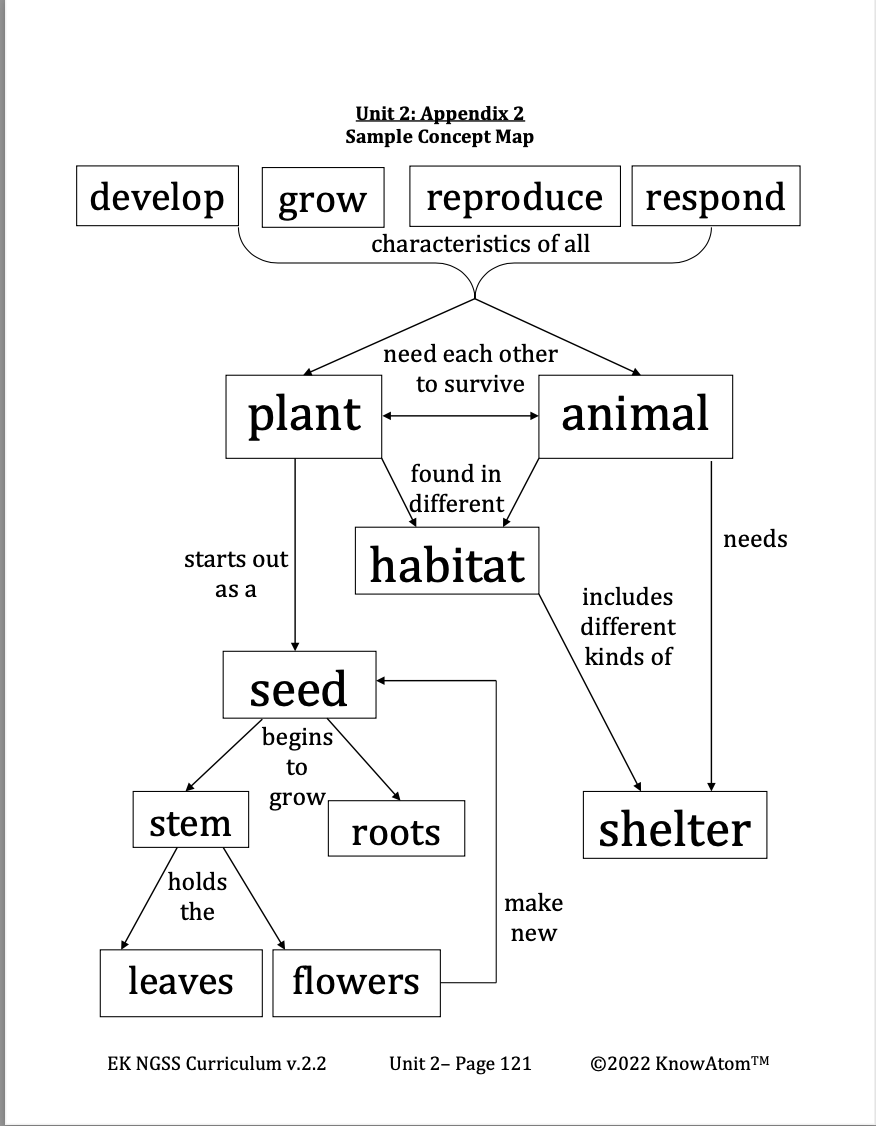
Science Vocabulary
Flowers : the parts of a plant that make seeds
Leaves : the parts of a plant that collect sunlight and make food
Plant : a living thing that makes its own food from sunlight
Roots : the parts of the plant that hold it in place and take in nutrients and water from the soil
Seed : a young plant inside a protective coat; needs air and water to grow
Stem : the part of a plant that holds the leaves and flowers in place; water and nutrients travel through the stem to the rest of the plant
Lexile(R) Certified Non-Fiction Science Reading (Excerpt)


Hands-on Science Activity
In this hands-on mini-lesson, students create a model sunflower plant to explore the structure and function of primary plant parts. After students build their plant models, they participate in a classroom discussion to explain each part of the plant using their model as a source of evidence. This process gives students a foundation of plant knowledge that will continue to serve them throughout this unit. In a subsequent lesson, students will use these plant models to further explore what plants need to live and grow.
Science Assessments
KnowAtom incorporates formative and summative assessments designed to make students thinking visible for deeper student-centered learning.
- Vocabulary Check
- Lab Checkpoints
- Concept Check Assessment
- Concept Map Assessment
- And More...

See How KnowAtom Aligns to NGSS Science Standards
Discover hands-on screens-off core science curriculum for student centered K-8 classrooms. KnowAtom supports classrooms with all hands-on materials, curriculum, and professional development to support mastery of the standards.

